It can often be assumed children will pick up how to write letters if they see them often enough (by osmosis). This is just not the case. Correct letter formation has to be taught. Seeing a completed letter or word or watching it being typed up and appear on a screen does not show children how to form the letters.
For children to develop a good handwriting style it is important to learn how to form letters correctly to begin with as this makes the transition from single letter formation to joined letter handwriting much easier. This enables them to develop a speedy, fluid and legible handwriting style.
Department of Education; The writing framework: July 2025; page32 & 33; https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-writing-framework now recognizes and highlights the importance of teaching correct letter formation from the very beginning, so, starting in foundation stage:
“It should be:
- • daily, until pupils can write legibly and easily
- • taught in small steps, with lots of opportunity for practice
- • cumulative: teachers should build on what pupils have learned previously
- • consolidated before teaching moves on so that pupils do not practise letters incorrectly
- • revisited when further practice is needed
- • demonstrated by the teacher
- • additional to any handwriting that forms part of teaching phonics”
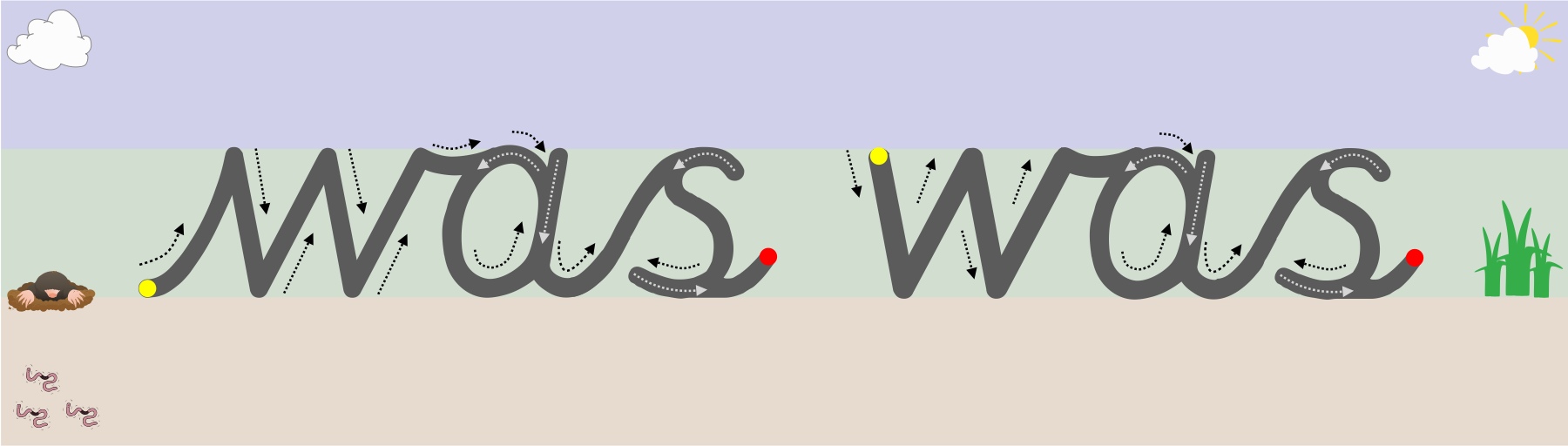
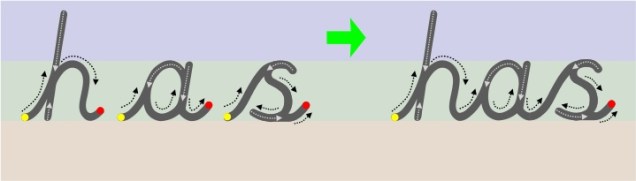
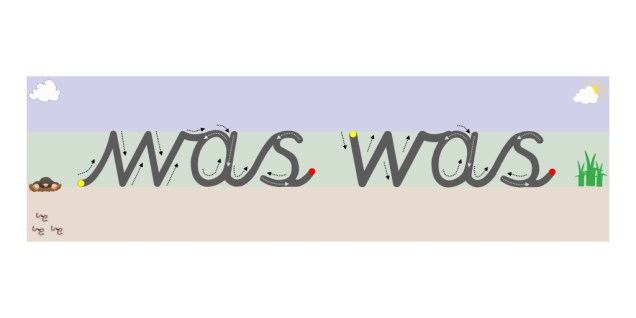
Letters are created through joining lines and curve shapes in a particular way. They have a designated start point and set directional pushes and pulls of the pencil to reach the designated finish point. This is why from the very start (2012) Teach Handwriting has always taught letter formation in groups/families rather than in alphabetical order (a Year 1 national curriculum statutory requirement in 2015). Certain groups use the same, or similar, shape and directional push and pulls of the pencil to form the letter, for instance the letter c has the same start point and anti-clockwise directional movement shape that is needed to create the letters a, d, g, o and, though a little more complicated, the letters s and e. Teaching letters in groups and families can also help to limit letter reversals such as b and d.
Another interesting and very important useful point included in the “Department of Education; The writing framework: July 2025; page 33; https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-writing-framework, for Year 1 is that:
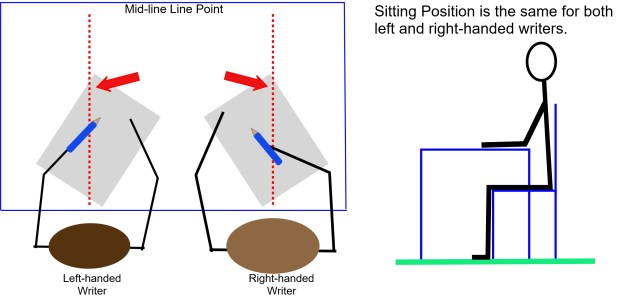
“Wide-lined paper is essential at this stage. Mid-line guides can also help pupils to position letters. Pupils should be introduced to paper with narrower lines once they can write legibly and easily on wide-lined paper.”
Which I believe, acknowledging the fact that children can form their letters correctly if taught correctly but may not be ready for narrow line height paper due to their developmental stage of their fine motor skill.
Also, it explains how in Year 2:
“To join letters easily and legibly, pupils first need to form the shape of each letter correctly, starting and finishing each one at the correct point and ensuring that its size is properly related to other letters in the same family.”
Due to how handwriting has or hasn’t been taught over the generations we all have our own way of handwriting. When supporting and teaching young children we need to develop a consistent approach so that they do not get confused or frustrated by adults giving them conflicting information.
For parents this means finding out from your child’s school which letter font they are teaching so that you can support them more effectively at home. This may mean that you have to learn a new way of writing some letters.
This also applies to teachers and teaching assistants; “Department of Education; The writing framework: July 2025; page 32; https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/the-writing-framework states:
“Teachers’ own handwriting should provide a model of high standards, across the curriculum and not just in handwriting lessons, but particularly when pupils are learning to write.”
As the adults in the situation, we have to accept that it is for us to make the changes. Just because something is different to the way we were taught, or do it, doesn’t mean it is wrong, it is just different!
Our free letter animations are not just to support children with their learning but also to provide parents and teachers (all adults really) with the knowledge and support to help children develop a consistent handwriting style.
Parent animation link: https://teachhandwriting.co.uk/parents.html
Teacher animation link – click through on the Key Stage you are teaching: https://teachhandwriting.co.uk/teach-handwriting-teachers.html