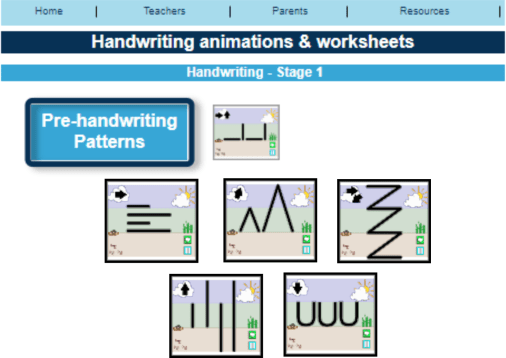
On our Teach Handwriting website and Scheme, as well as on our Teach Phonics website, children are taught the letter names to begin with. Some schools, teacher and parents still seem to be concerned that this is not consistent with the teaching of phonics.
A myth which seems to have become popular, since the introduction of phonics into schools, is that children should not be taught the alphabet letter names as they find it too confusing. However, there is no evidence to suggest this is true. The Independent review of the teaching of early reading, final report, Jim Rose March 2006 states:
“The teaching of letter names is often left until after the sounds of the letters have been learned, in the belief that it can be confusing for children to have to learn both together. However, research indicates that children often learn letter names earlier than they learn letter sounds and that five year olds who know more letter names also know more letter sounds. The reasons for this are not fully understood by researchers’.
Given that children will meet many instances outside, as well as within, their settings and schools where letter names are used, it makes sense to teach them within the programme of early phonic work.
It appears that the distinction between a letter name and a letter sound is easily understood by the majority of children.” (Page 26)
Rose, cites Professor Morag Stuart who suggests that:
‘…children expect things to have names and are accustomed to rapidly acquiring the names of things.’ (Independent review of the teaching of early reading’ final report, Jim Rose March 2006, page 27.)
Learning the unique letter names of the alphabet is a pre-phonics skill; as well as an early learning goal. It has to be remembered that a letter is a shape which only represents a sound when it is placed within a word or sentence. Also a letter or combination of letters can represent more than one sound and so the only unique way of identifying alphabet letters when we talk about them is to use their names.
Learning the correct letter names helps to reinforce that when talking about the letter ‘a’ (ay) for example it has a set shape regardless of the sound that it will be representing in the word. This further supports children’s handwriting development as the communication of your requirements is unambiguous.
One of the first things we like a child to be able to write correctly is their name, however most names are impossible to spell using the simple phonics code taught to young children. A name does not have to be long in length to be phonetically difficult to spell such as Christopher or Charlotte. Shorter names such as Lucy or Liam also cause a problem.
The only logical answer I suggest is to use the letter names until a child has been introduced to the more complex phonics coding system.