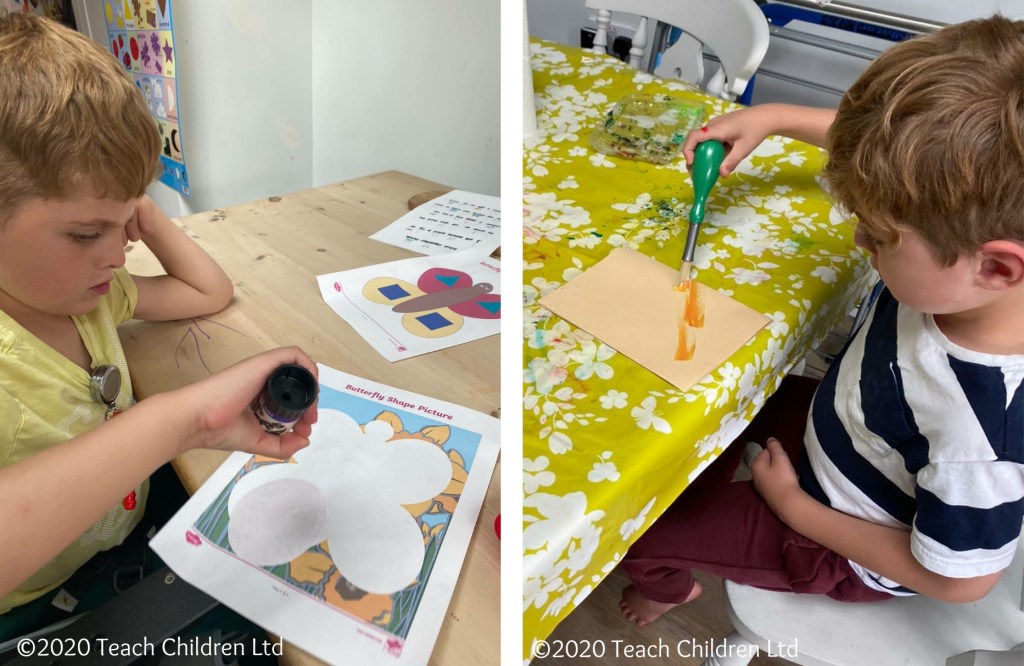
Hand dominance is where one hand has more influence or control than the other. This is sometimes referred to as hand preference, where one hand is preferred or chosen over the other, as it is more reliable in performing a range of skilled activities (handedness).
Children tend to develop hand dominance between the ages of 3-5 years old, for some it may be slightly later and for a few it does not become a subconscious decision until they are 8 or 9 years old. Many children will naturally develop a clear right or left-hand dominance which is greatly influenced by their genetics.
Some can develop a mixed dominance; this is where a child finds they have more control and greater skills for handwriting with say the left hand but prefer and display more precise skills with the right hand in tasks such as using scissors. Studies have shown handedness can be based on the type of muscles used in controlling gross and fine motor skills for completing particular tasks. The control of various muscle types is located in different hemispheres of the brain. Those relating to dexterity (fine motor skills), required for writing, are strongly related to hand dominance, whereas the larger muscle groups (gross motor skills), involving strength, rely less on hand dominance.
Whether a child is right or left-handed does not affect their academic ability or progress, if they have developed and been taught the appropriate key skills. The important thing is not to force particular hand dominance on a child. It will never feel natural for them and the acquisition of gross and fine motor skills will feel awkward and may well appear clumsy, delaying their development, skills ability, confidence and self-esteem.
Only about 1% of the population are truly ambidextrous, which means they are able to perform tasks using either hand with equal skill and proficiency; a rare trait indeed.
Our link to games ideas to help develop and support hand dominance: https://teachhandwriting.co.uk/hand-dominance.html