Teaching your child the vocabulary related to placement (preposition) and direction is import in supporting them to understand and follow instructions, as well as sharing information themselves, such as; ‘put your cup on the table’ or to say ‘teddy in car’.
We also use this placement (preposition) and directional language to explain how to draw shapes, patterns and write letters and numbers.
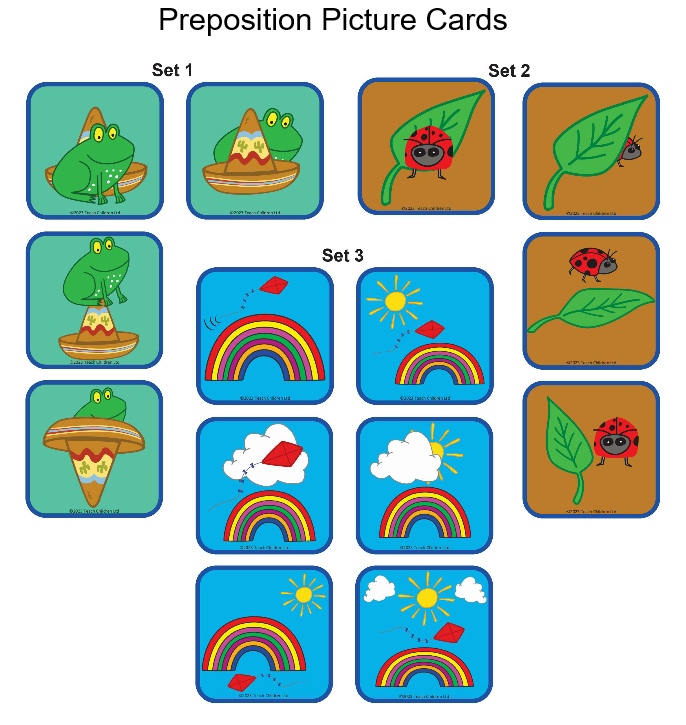
We have created three sets of picture cards and games to help you support your child in developing and using positional (preposition) and directional vocabulary.
You can find these free resources on our Phonics website by following this link: https://www.teachphonics.co.uk/phonics-resources.html
You can find these free resources in Parent section of the Teach Handwriting website by following this link: https://teachhandwriting.co.uk/more-activities.html
What are prepositions?
“A word used with a noun or pronoun to show place, position, time or means, e.g. at home, in the hall, on Sunday, by train.” Definition from Oxford School Dictionary, third edition 2002.
Here are just some preposition and directional phrases you might like to use:
On the … On top of the … Above the … Over the…
Under the… Below the … Beneath … Underneath …
Behind the …
In front of the…
Next to …Beside the … On the right of … To the right of … On the right-hand side … On the left of … To the left of … On the left-hand side… Before the … After the …
In the… Inside the …
Out of the … Outside of the …
Between the … In between the … In the middle … In the center …
Going up the …. Going down the … Going towards the… Going away from …