We would recommend teaching joins in join type groups, whether your child has learnt cursive or continuous cursive single letter fonts.
Teaching the join types in their groups helps a child to understand the directional pushes and pulls required to successfully join the different letter combinations.
There are 4 main groups of letter joins; bottom joins, bottom to “c” shape joins, “e” joins (top and bottom join strokes) and top joins.
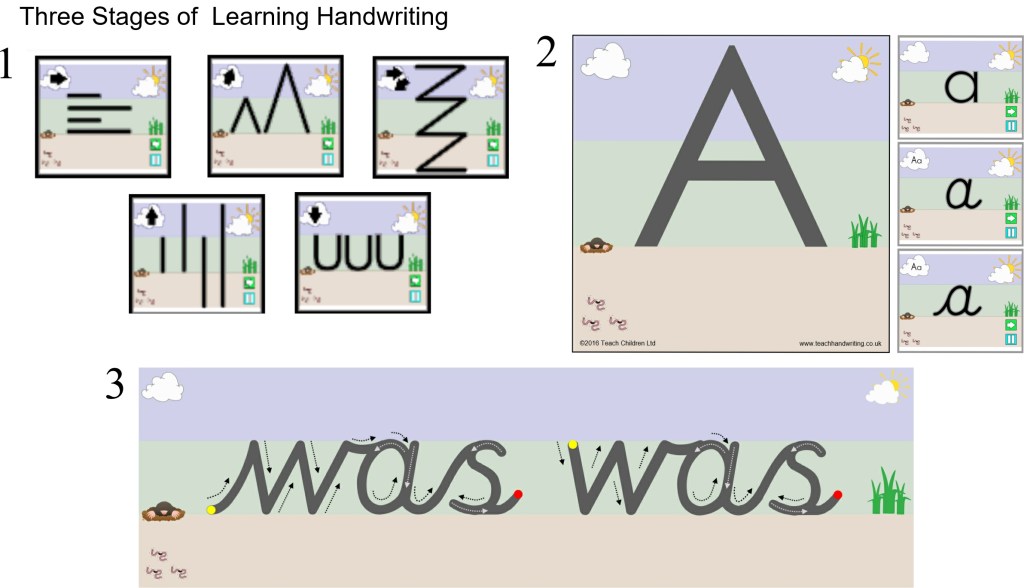
Moving from Cursive Single Letters to Joining
There are seven join strokes to be taught. Most children will find the bottom joins the easiest to achieve, as it only requires the extension of the exit stroke they already put on the letters. The bottom to “c” shape joins can be tricky at first but soon mastered. The joins that tend to cause the most confusion and difficulty are the “e” joiners and top exit joiners.
I would recommend teaching the bottom joins first, then the ‘e’ joins and finally the top exit letter joins.
Moving from Continuous Cursive Single Letters to Joining
There are three join strokes to be taught. The easiest is the bottom exit letters (the majority of the letters), all a child has to do is write the letters closer together without lifting their pencil off the paper. Only the top to “e” and top joiners need to be taught for continuous cursive, as the nature of the font style means that the lead-in and exit strokes needed to join the majority of letter combinations have already been taught.
I would recommend teaching the bottom joins first, then the top exit to ‘e’ join and finally the top exit letter joins.
The ultimate aim is for a child to develop a good handwriting style; which means;
• They can produce and maintain a good speed
• Have a fluid hand movement that is comfortable
• Letters are of a consistent and appropriate size, positioned correctly
• Handwriting is legible (so others can read it easily).
It is important to remember that for some children (mainly SEND pupils) this may mean that they will always print or use a single letter form of writing as learning to join is just not appropriate. But that does not mean they will not comply with the bullet points above.
Have you got your Free Join Animations & Worksheets?
For Teachers: https://teachhandwriting.co.uk/key-stage-2-handwriting-routes.html
For Parents: https://teachhandwriting.co.uk/parents.html